 |
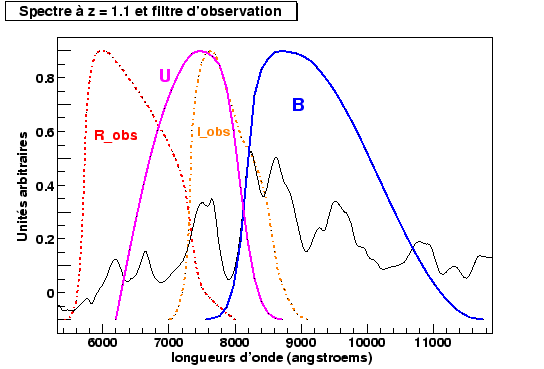
Both supernovæ most remote of our batch with a shift towards the red around 1 were mainly observed in filter I correspondent with the filter U in the reference frame of the supernova (figure 10.10 ). We thus will use the close supernovæ observed out of U to build a new estimator of distance.
 |
We will apply the same method as for the observations out of B
and out of V We will use from now on the magnitude U in the reference
frame of the supernova like estimator of distance and the color ![]() to estimate a new relation of standardization.
to estimate a new relation of standardization.
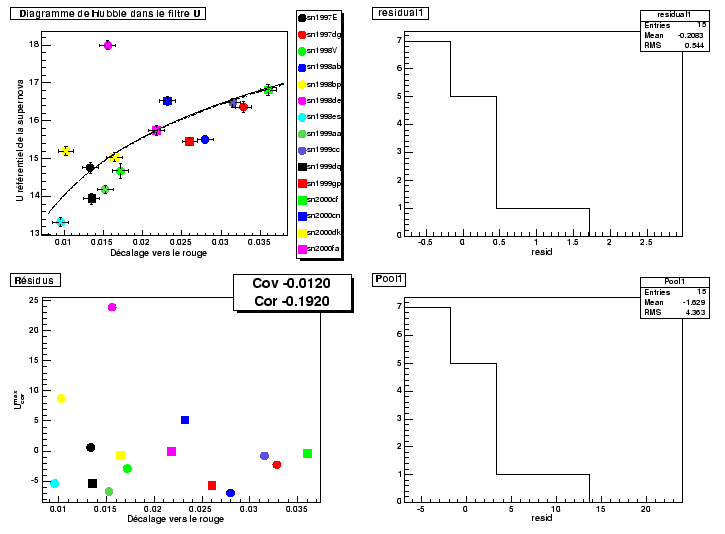
We have for that about fifteen supernovæ whose redshifts are larger than 0.01. The parameters of their lightcurve are given in C.2 10.11 shows their diagram of Hubble out of U not corrected for the color and the factor of stretching. We find a dispersion before correction 0.54 magnitude, that is to say the same order of magnitude as in the filter B.
 |