Contents
As we saw earlier, the supernovæ of the Ia type present neither
hydrogen, nor helium in their spectrum, whereas these elements
represent more than 99% of the nuclear matter of the universe. The
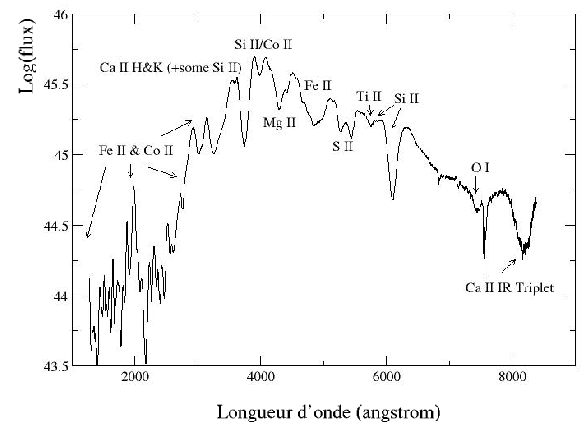
supernovæ of the Ia type are characterized by a very strong silicon
emission ionized once (SiII). It is the emission of this element with
6100 angstroems which is the clearest signature of the types Ia. many
other elements of intermediate mass are observed (magnesium, calcium or
sulphur) at the time of the maximum of luminosity. They leave room with
cobalt and nickel in the following weeks, for finally being dominated
by fine-grained iron the phase nébulaire a few months after the
explosion. Another significant characteristic of the spectra, is the
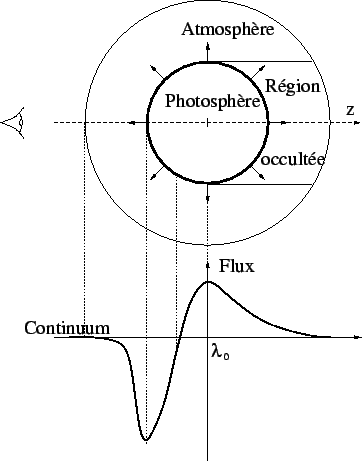
presence of P-Cygni profiles (Figure 5.1 ) very broad indicating speeds of expansion of the very large external layers (of 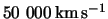 ).
).
Figure 5.1: Profile says P-Cygni
(bearing the name of the star hypergéante P Cygni) of the lines formed
within an atmosphere expanding. This one is seen by the observer partly
in projection on photosphere (it also expanding in the case of a
supernova) which forms the continuous spectrum -- from where a
component in absorption shifted towards blue -- and partly apart from
the heart -- what gives a component in emission centered over the
wavelength at rest 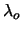 .
The more the speed of expansion of photosphere is raised, the more the
profile is `` dilated '' in wavelength, and the more the minimum of
absorption is shifted towards blue, the not moving emission peak. The
height of the emission and absorption lines is directly connected to
the optical depth: the higher this one is, the more absorption and the
emission will be strong until the line becomes saturated if the optical
depth is too high. This figure as its legend are extracted from
blanc2002.
.
The more the speed of expansion of photosphere is raised, the more the
profile is `` dilated '' in wavelength, and the more the minimum of
absorption is shifted towards blue, the not moving emission peak. The
height of the emission and absorption lines is directly connected to
the optical depth: the higher this one is, the more absorption and the
emission will be strong until the line becomes saturated if the optical
depth is too high. This figure as its legend are extracted from
blanc2002.
|
Lastly, the spectra do not have until now little or not shown
polarization, which would tend to show that these phenomena are
spherical (howell2001, kasen2003 and wang2003).
Figure 5.2: Spectrum of typical SN1981B of the supernovæ of the Ia type to the maximum of luminosity (drawn from nugent199ä).
 |
Contents Julien Raux 2004-05-04
![]() ).
).