Current measurements indicate that ![]() 2. In this range of redshift, the flood of Hubble is
largely reached. Moreover, this range of redshift makes it
possible to trace the evolution of the density of black energy over all
the period when it prevails. Beyond 2, the matter becomes dominant and
determines the expansion. Lastly, the evolution according to the shift
towards the red could make it possible to measure a possible evolution
of the equation of state .
2. In this range of redshift, the flood of Hubble is
largely reached. Moreover, this range of redshift makes it
possible to trace the evolution of the density of black energy over all
the period when it prevails. Beyond 2, the matter becomes dominant and
determines the expansion. Lastly, the evolution according to the shift
towards the red could make it possible to measure a possible evolution
of the equation of state .
Measurements of the anisotropies of the cosmological diffuse bottom
have a limited capacity, measurements which could be made by the
satellite dedicated Planck will be able as well as possible to reach
precise details of about 10%. Moreover, these measurements have only
one lever limited in spectral shift, and will not be able to make of
differential measurement of ![]() by considering an intrinsic uncertainty of the luminosity of 14%
(aldering2002). Moreover, if one manages to measure ind├ępendemment
by considering an intrinsic uncertainty of the luminosity of 14%
(aldering2002). Moreover, if one manages to measure ind├ępendemment ![]() of 0.16.
of 0.16.
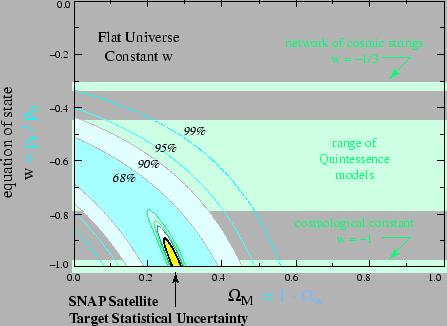 |
The methods of counting of galaxies and cluster have the same precision potentially as the supernov├Ž of the type Ia. Cependant, with many problems the systematic ones sully this type of measurement and measurements strongly depend on the models considered.
Lastly, the measurement of the effects of lenses weak on a surface of ![]() (huterer2002).
(huterer2002).