The astronomers work quasi exclusively in term magnitude to quantify the brightness of an object. The majority (if they all are not) measurable quantities are expressed in this system (zero points, brightness of the bottom of sky, etc...).
It is pointed out that the magnitude of an object is defined like:
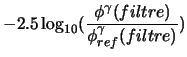 |
(7.8) | ||
| Â | 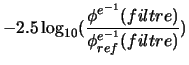 |
(7.9) |
| (7.10) |
where ![]() the star of reference in the system magnitude considered indicates.
the star of reference in the system magnitude considered indicates.
Our signal on noise is thus reexpressed:
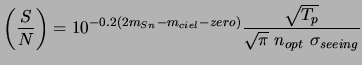 |
(7.11) |
To select the most significant objects, a cut which we will call ![]() ,
it corresponds to the value for which the number of Poissonnian
fluctuations which exceed the cut of the same order of magnitude as the
number of supernovæ is awaited (about 1 by CCD).
,
it corresponds to the value for which the number of Poissonnian
fluctuations which exceed the cut of the same order of magnitude as the
number of supernovæ is awaited (about 1 by CCD).
While considering ![]() , one can define a limiting magnitude of detection:
, one can define a limiting magnitude of detection:
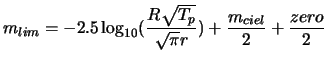 |
(7.12) |
By considering conditions of seeing and a similar duration, the
doubling of the diameter of the mirror of the telescope makes it
possible to gain ![]() magnitude.
magnitude.